Revolutionizing Obesity Treatment: How Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) Offers a Minimally Invasive Path to Better Health
In the quest for effective weight loss solutions, Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) stands out as a groundbreaking option. This minimally invasive procedure, also known as endoscopic gastric sleeve, is reshaping the landscape of obesity treatment. Unlike traditional surgical methods, ESG offers a less invasive path to significant weight loss, making it an attractive option for those striving for better health. In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve into the details of ESG, exploring its process, benefits, and long-term impact on health and weight management.
Navigating the World of ESG
1. What is Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG)?
2. How Does ESG Compare to Gastric Bypass?
3. Who is an Ideal Candidate for ESG?
4. The ESG Procedure: A Detailed Walkthrough
5. Expected Results: What Can ESG Achieve?
6. ESG vs. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy: Understanding the Differences
7. BMI Requirements for ESG: Are You Eligible?
8. Life After ESG: Diet, Exercise, and Long-term Management
9. Safety and Risks of ESG: What You Need to Know
10. ESG and Gastric Bypass Revision: Is It an Option?
1. What is Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG)?
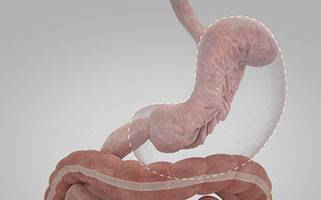
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty, popularly known as ESG, is a minimally invasive weight loss procedure that utilizes an endoscope equipped with a suturing device. This technique involves reducing the stomach’s size to limit food intake and promote early satiety. Unlike traditional surgeries, ESG is performed without any external incisions, offering a quicker recovery and fewer complications.
2. How Does ESG Compare to Gastric Bypass?
While both ESG and gastric bypass aim at weight loss, they differ significantly in their approach. Gastric bypass is more invasive, involving rerouting and cutting the stomach and intestines, whereas ESG restricts stomach size using internal sutures. ESG typically has fewer risks and a quicker recovery, making it a suitable alternative for many patients.
3. Who is an Ideal Candidate for ESG?
Ideal candidates for ESG are individuals with a BMI between 30 and 40, who have struggled with weight loss through traditional methods like diet and exercise. It’s also an option for those who may not qualify for more invasive bariatric surgeries or who prefer a less invasive approach.
4. The ESG Procedure: A Detailed Walkthrough
The ESG procedure is performed under general anesthesia. A flexible endoscope with a camera and suturing device attached is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach. The endoscopist then places a series of sutures in the stomach to create a narrow sleeve, reducing its capacity. This outpatient procedure usually takes about 1-2 hours, and most patients can go home the same day.
5. Expected Results: What Can ESG Achieve?
Patients undergoing ESG can expect significant weight loss, often losing 15-20% of their total body weight within the first year. The procedure also helps in improving obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure. Long-term success depends largely on adherence to a healthy lifestyle post-procedure.
6. ESG vs. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy: Understanding the Differences
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG) involves surgically removing a portion of the stomach, whereas ESG reduces stomach size through internal sutures. LSG is more invasive and requires a longer recovery period compared to ESG, which is performed endoscopically and is less invasive.
7. BMI Requirements for ESG: Are You Eligible?
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a key factor in determining eligibility for ESG. Typically, candidates have a BMI between 30 and 40. However, each individual’s case is unique, and consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to determine suitability.
8. Life After ESG: Diet, Exercise, and Long-term Management
After ESG, patients are advised to follow a structured diet starting with a liquid diet, gradually transitioning to solid foods. Regular exercise and healthy eating habits are crucial for maintaining weight loss. Long-term success also requires psychological and nutritional counseling.
9. Safety and Risks of ESG: What You Need to Know
ESG is generally safer than more invasive bariatric procedures, with a lower risk of complications like infections or hernias. However, potential risks include nausea, abdominal pain, and in rare cases, suture line leaks. It’s important to have regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider.
10. ESG and Gastric Bypass Revision: Is It an Option?
ESG can be an option for patients seeking revision of a previous gastric bypass. It’s particularly appealing due to its minimally invasive nature and reduced risk profile compared to surgical revision options.
Key Takeaways
– ESG is a minimally invasive, endoscopic weight loss procedure.
– Suitable for individuals with a BMI of 30-40, seeking an alternative to traditional surgeries.
– Offers significant weight loss and improves obesity-related health conditions.
– Requires commitment to a healthy lifestyle for long-term success.
– Generally safer with fewer risks compared to more invasive bariatric surgeries.
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) represents a significant advancement in weight loss treatments, offering a less invasive, yet effective alternative to traditional surgeries. This procedure is not just about losing weight; it’s about embracing a healthier lifestyle and improving overall well-being. If you’re considering ESG, consult with a healthcare professional to determine if it’s the right option for you.
